Microgrids

The electric grid is a network of poles, power lines and substations that deliver electricity from generating resources to homes and businesses. The grid is essential for modern life, supporting everything from lighting to technology.

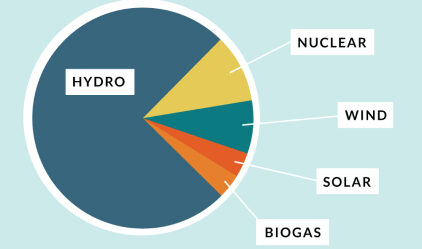
Wind power is a form of renewable energy that converts the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy using wind turbines.
Fun fact: The PUD receives nearly 10% of its power from multiple wind farms in central Washington and Oregon.

Solar energy comes from the sun. We use special panels called solar panels to catch sunlight and turn it into electricity. This electricity can power our homes, schools, and gadgets. It’s a clean and endless source of energy, which helps keep our planet healthy.

Hydroelectric power is a renewable energy source that generates electricity using the natural flow of moving water.
Fun fact: Hydropower can be generated using a dam and reservoir like the PUD’s Jackson Project or “damless” run-of-the-river facilities like the PUD’s Young’s Creek Project.

Battery energy storage systems, or BESS, store energy like reservoirs store water. They capture excess energy from renewable sources like solar and wind when it’s available and release it when needed.
Fun fact: It would take 10 Teslas to store the same energy as what’s in the 1000kW storage system seen above.
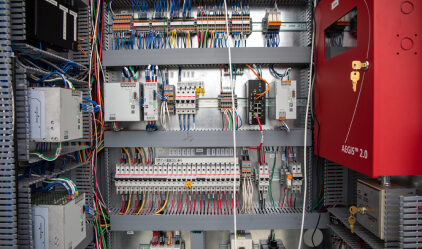
A microgrid control center manages operation of a microgrid, ensuring efficient and reliable power distribution.
It monitors components, controls the flow of electricity and optimizes energy use, both when linked to the grid or in “island mode.”

From an object of curiosity to a cornerstone of daily life, electricity is exciting. It eases workloads, helps us stay connected and even lights up our nights. Its potential continues to unfold and is up to the next generation to discover.